Logistics and Regulations in International Heavy Machinery Shipping

Shipping heavy machinery internationally presents unique logistical hurdles beyond those encountered in standard freight transport. The sheer size and weight of these items necessitate specialized handling, transport methods, and careful planning to ensure safe and efficient delivery. Furthermore, navigating the complex web of international regulations and customs procedures adds significant complexity to the process.
Logistical Challenges in International Heavy Machinery Transport
The transportation of oversized and heavy machinery across international borders involves numerous logistical complexities. These include finding suitable vessels or transport vehicles capable of handling the weight and dimensions of the equipment, securing appropriate permits for oversized loads on roads and bridges, and planning efficient routes to avoid potential delays or damage. The need for specialized loading and unloading equipment, including cranes and heavy-lift vehicles, further complicates the process.
Moreover, ensuring the machinery’s securement during transit is crucial to prevent damage or accidents. For example, a large excavator shipped from Europe to South America might require a specialized roll-on/roll-off vessel, and careful planning to account for port infrastructure limitations at both ends of the journey. Improper securing could result in damage during transit, incurring significant repair costs and delays.
Permits, Licenses, and Documentation for International Heavy Machinery Shipment
A multitude of permits, licenses, and documents are required for the international shipment of heavy machinery. These documents vary depending on the origin and destination countries, the type of machinery being shipped, and the mode of transport. Essential documents typically include export licenses from the country of origin, import permits for the destination country, bills of lading, certificates of origin, insurance documents, and packing lists.
Furthermore, specific permits may be required for oversized or hazardous cargo, including detailed specifications of the machinery’s dimensions, weight, and any potential hazards it poses. Failure to obtain all necessary documentation can lead to significant delays, fines, or even the seizure of the cargo. For instance, a shipment of mining equipment from Canada to Australia would require compliance with both countries’ stringent regulations concerning environmental protection and safety standards, necessitating specific permits and certifications.
Customs Regulations and Procedures in Different Countries
Customs regulations and procedures vary considerably between countries, impacting the efficiency and cost of international heavy machinery shipping. Import duties, taxes, and tariffs differ widely, depending on the type of machinery, its country of origin, and the destination country’s trade policies. Different countries also have varying requirements for customs inspections and documentation. Some countries may have stricter regulations regarding the importation of used machinery compared to new equipment.
For example, importing a used bulldozer into the European Union might involve more stringent environmental compliance checks than importing a new one into the United States. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate cost estimation and efficient customs clearance.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Obtaining Necessary Permits and Clearances
Obtaining the necessary permits and clearances for transporting heavy machinery internationally is a multi-step process that requires meticulous planning and attention to detail.
- Initial Assessment and Route Planning: Determine the optimal shipping route, considering factors such as distance, infrastructure limitations, and potential delays.
- Documentation Preparation: Gather all necessary documentation, including export licenses, import permits, bills of lading, certificates of origin, and insurance policies. This often involves significant research and interaction with government agencies in both the origin and destination countries.
- Customs Broker Engagement: Engage a reputable customs broker familiar with the regulations in both the origin and destination countries. They can assist with navigating complex customs procedures and ensure timely clearance.
- Permit Applications: Submit all necessary permit applications to the relevant authorities in both countries, addressing any specific requirements for oversized or hazardous cargo.
- Shipping Arrangement: Arrange for transportation, considering the size and weight of the machinery and selecting the most appropriate mode of transport (sea, land, or air). This includes coordinating with specialized carriers experienced in handling heavy machinery.
- Loading and Securing: Ensure the machinery is properly loaded and secured for transit, minimizing the risk of damage or accidents during transport.
- Customs Clearance: Work with the customs broker to ensure smooth customs clearance at both the origin and destination ports or borders.
- Delivery and Inspection: Upon arrival, inspect the machinery for any damage incurred during transit and complete the necessary documentation.
Potential delays can arise from various factors, including incomplete documentation, unforeseen customs inspections, port congestion, or unexpected logistical challenges. Solutions include proactive communication with all parties involved, contingency planning for potential delays, and engagement of experienced logistics professionals who can anticipate and mitigate potential problems. For example, having backup transport options ready can significantly reduce delays caused by unforeseen circumstances.
Types of Heavy Machinery and Specialized Transport Methods

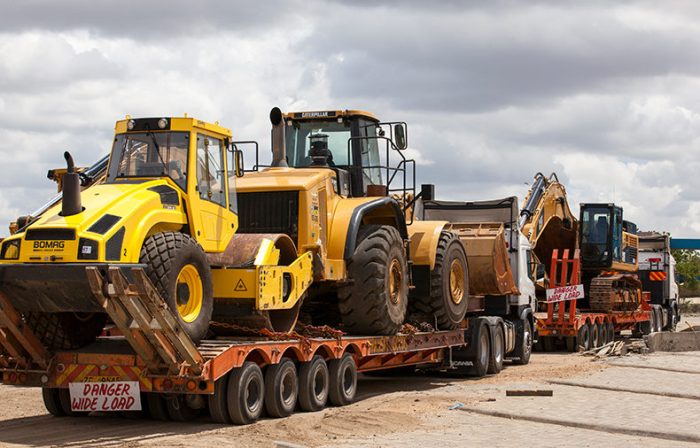
International transport of heavy machinery requires careful consideration of the equipment’s type and the most suitable method for its safe and efficient movement. Different machines necessitate different approaches, encompassing specialized handling, packaging, and shipping techniques to mitigate risks and ensure timely delivery. This section details the common types of heavy machinery, their associated transport methods, and best practices for securing them during transit.
Categorization of Heavy Machinery for International Transport
Heavy machinery transported internationally falls broadly into three categories: construction equipment, mining equipment, and industrial machinery. Each category encompasses a diverse range of machines with varying sizes, weights, and structural characteristics, influencing the choice of transport method. Construction equipment includes excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and pavers; mining equipment involves excavators, haul trucks, drills, and crushers; while industrial machinery encompasses a wide variety of equipment depending on the industry, such as transformers, generators, and large manufacturing equipment.
The selection of transport method is crucial for minimizing damage, delays, and costs.
Specialized Transport Methods for Heavy Machinery
The choice of transport method depends heavily on the size, weight, and fragility of the machinery. Several options exist, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Flat Rack Containers: These open-top containers are ideal for oversized or oddly shaped machinery that wouldn’t fit into a standard container. They allow for flexible loading and unloading. Securing is crucial and usually involves lashing and bracing the equipment to the container frame.
- Roll-on/Roll-off (RoRo) Ships: These vessels allow for the direct loading and unloading of wheeled equipment via ramps. This method is efficient for self-propelled machinery like bulldozers and excavators. Securing involves wheel chocks and other restraints to prevent movement during transit.
- Heavy-Lift Vessels: For extremely large and heavy machinery, specialized heavy-lift vessels are necessary. These vessels utilize powerful cranes to load and unload equipment directly onto the deck. The securing methods here are highly specialized and depend on the specific characteristics of the cargo and the vessel.
- Breakbulk Shipping: This method involves loading individual pieces of machinery directly onto the ship’s deck without containers. It’s suitable for very large or unusually shaped equipment that cannot be containerized. Securing is critical and often involves specialized rigging and lashing techniques.
Packaging and Securing Methods for Heavy Machinery
Proper packaging and securing are paramount to prevent damage during transit. Methods vary depending on the type of machinery and transport method used.
- Crating: Custom-built wooden crates provide excellent protection against impact and moisture damage. Internal bracing is essential to prevent shifting during transit. Crates are commonly used for smaller, more fragile components.
- Lashing and Securing: This involves using straps, chains, and other tie-downs to secure the machinery to the transport vehicle or container. Proper tensioning is vital to prevent movement. The specific techniques vary based on the type of equipment and the transport method.
- Protective Coatings: Applying protective coatings, such as anti-corrosion paints or wraps, can protect the machinery from moisture, rust, and abrasion during transit. This is particularly important for equipment shipped overseas or in harsh weather conditions.
- Shock Absorption: For delicate components, shock-absorbing materials like rubber pads or foam can be used to minimize vibrations and impacts during transport. This is often used in conjunction with crating or other securing methods.
Infographic: Heavy Machinery Transport Methods
The infographic would feature a clean, modern design using a predominantly blue and grey color scheme to convey professionalism and reliability. The font would be a sans-serif typeface like Arial or Calibri for easy readability.The layout would be divided into three main sections, one for each category of heavy machinery (Construction, Mining, Industrial). Each section would feature icons representing common types of machinery within that category (e.g., an excavator for construction, a haul truck for mining, and a large gear for industrial).
Arrows would connect each machinery icon to a corresponding transport method icon (e.g., a flat rack container, a RoRo ship, a heavy-lift crane). A color-coded key would clarify the meaning of each icon and transport method. The overall style would be simple and visually appealing, avoiding clutter to ensure clarity and easy understanding of the information presented.